时间复杂度与空间复杂度
时间复杂度与空间复杂度用来衡量算法的性能,算法可能在一定时间内都需要不断优化,优化过程需要同时兼顾代码可读性与代码运行性能。
时间复杂度我们一般使用大 O 表示法,常见时间复杂度表示如下所示:
性能由上至下一次降低。
空间复杂度我们一般使用大 S 表示法,例如
栈
栈是非常常见的一种数据结构,很多算法中都需要使用栈作为辅助。栈的特性可归纳为:
- 先进后出
常见栈的应用有:
- 括号匹配
- 作为工具,用于遍历数或图
经典题
请使用栈完成二叉树的前序遍历
function traverse(root) {const res = [];const stack = [];if (root) stack.push(root);while (stack.length) {const n = stack.pop();res.push(n.val);const { left, right } = n;if (right) stack.push(right);if (left) stack.push(left);}return res;}
队列
队列用于解决先进先出的问题,保证有序性。在 JavaScript 异步处理中,存在任务队列以调度异步任务。
常见队列的应用有:
- react 中的调度
- 任务队列
经典题
请使用队列统计最近请求次数
function RecentCounter() {this.q = [];}RecentCounter.prototype.ping = function(t) {this.q.push(t);while (this.q[0] < t - 3000) {this.q.shift();}return this.q.length;};
浏览器 JavaScript 中的事件队列
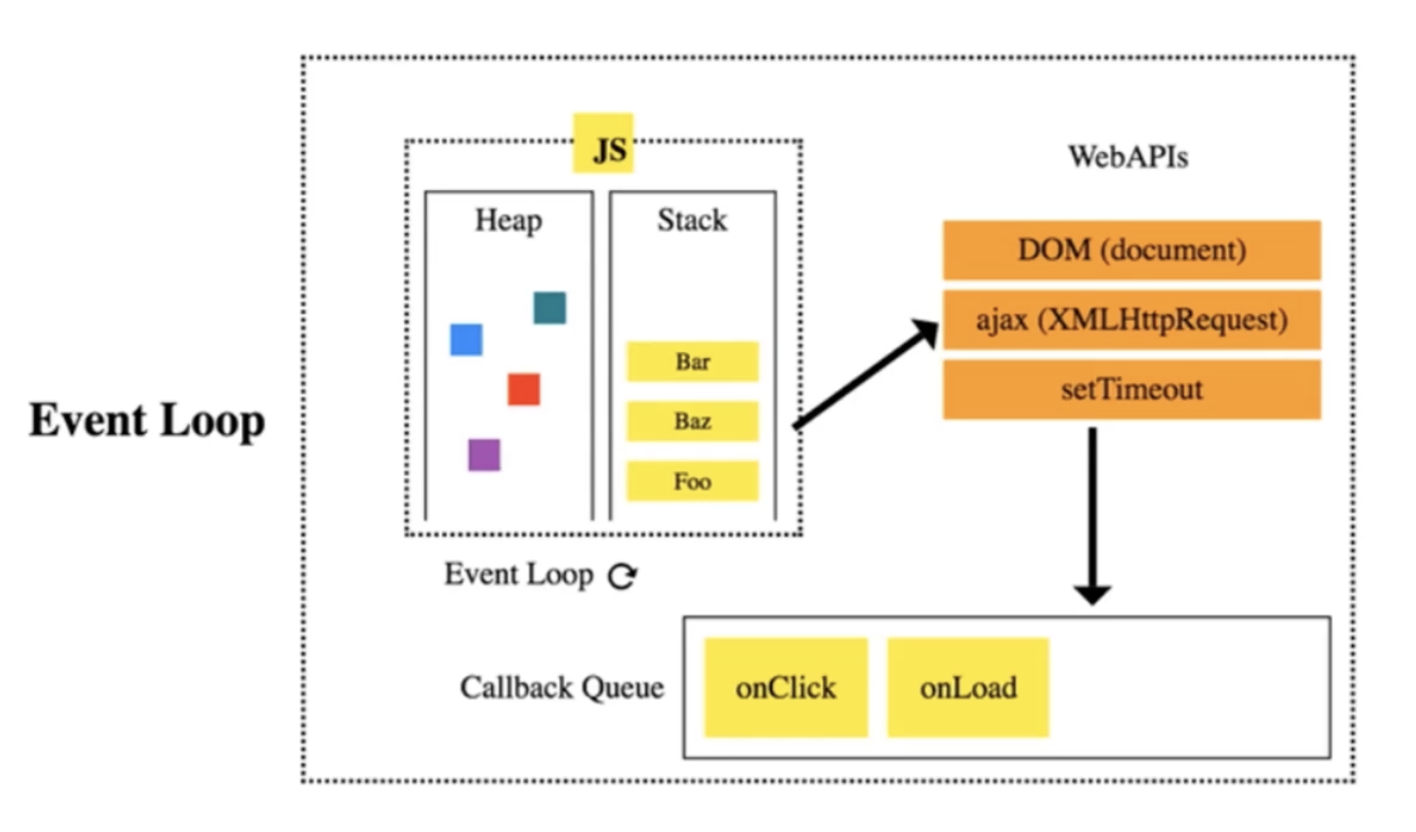
链表
链表可用于存储不连续的数据,通常前后节点的关系使用指针来确立(next),在有些场景下链表中每个节点上可能既存在前指针,又存在后指针。普通链表示例如下:
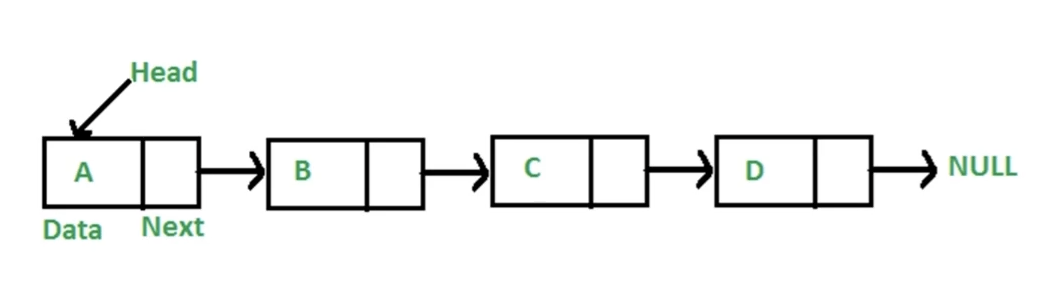
对于链表相关的算法,常用的技巧有一下几点:
- 双指针【反转链表】
- 快慢指针【判断链表是否有环】
经典题
反转链表
反转链表运用到了双指针的技巧,整体分析可能会觉得比较复杂,我们不妨两个节点一分析,链表的反转其实是将前后两个节点顺序交换,最终输出生成后的链表。
function reverse(head) {// 首先建立两个指针let p1 = head;let p2 = null;while (p1) {const temp = p1.next;p1.next = p2;p2 = p1;p1 = temp;}return p2;}
判断链表是否有环
判断链表是否有环是一个很经典的算法题,我们联想到解过的数学题,两个运动员同时从起点出发围绕跑到赛跑,跑得快可能会和跑得慢的运动员相遇,由此我们抽象出了两个指针——快慢指针,在遍历链表的过程中,快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步,若快慢指针相遇,则当前遍历到的为同一个节点。
function linkHasCycle(head) {// 两个指针,快慢指针let p1 = head;let p2 = head;while (p1 && p2 && p2.next) {p1 = p1.next;p2 = p2.next.next;// 如果此时 p1 === p2,证明为同一个节点,即链表成环if (p1 === p2) {return true;}}return false;}
JavaScript 中原型继承的应用
请实现 instanceOf?
instanceOf 的原理是遍历原型链,通过对比原型链上的 proto 属性是否等于给定的 prototype,等于则返回 true,否则返回 false。
function instanceOf(A, B) {let p = A;while (p) {if (p === B.prototype) {return true;}p = p.__proto__;}return false;}// 进行验证instanceOf([], Array); // true
集合
JavaScript 也加入了集合的概念,即 Set,集合的特点为:
- 元素无重复
- 存储随机且不连续
我们通常使用 Set 来解决去重问题,辅助数组的一些操作。
const arr = [1, 2, 2, 3];const uniqArr = [...new Set(arr)]; // [1, 2, 3]
经典题
求两个数组的交集
给定两个数组:[1, 2, 2, 1]、[2, 2],输出两者交集 [2]。
function intersection(nums1, nums2) {return [...new Set(nums1)].filter(n => nums2.includes(n));}
字典
JavaScript 也加入了字典,即 Map,字典的特点:
- 满足 key-value 形式
- 随机存储
其中还有 WeakMap,弱引用,将对象作为键,利于垃圾回收。
经典题
求两个数组的交集
给定两个数组:[1, 2, 2, 1]、[2, 2],输出两者交集 [2]。这道题目我们可以使用字典来进行优化。即将 nums1 中的元素先添加到字典映射中,然后遍历 nums2,如果遍历到的元素在字典映射中有值则记录该值并将这个值从 nums2 中移除,以此求得两数组交集。
function intersection(nums1, nums2) {// const map;}
无重复字符的最长子串
给定一个字符串,求该字符串的无重复字符最长子串。使用双指针滑动窗口,当扫描到的左右指针对应的值相等时,则将左指针向右移动一位,最终右指针指向字符串最后一个值时,扫描结束,返回此时窗口所包含的子串。
function lengthOfLongestSubstring(s) {let l = 0;let len = 0;const map = new Map();for (let r = 0; r < s.length; r++) {// 获取当前右指针指向元素const e = s[r];const mapVal = map.get(e);if (map.has(e) && mapVal >= l) {// 此时将作指针移动到不重复的元素上l = mapVal + 1;}len = Math.max(len, r - l + 1);// 记录对应元素的索引map.set(e, r);}return len;}
最小覆盖子串
给定一个字符串 S,一个字符串 T,请在 S 中找到包含 T 所有字符的最小子串。
LeetCode 76 输入:s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC" 输出:"BANC
使用滑动窗口,定义左右指针,首先将右指针向右移动。
/*** 给你一个字符串 s 、一个字符串 t 。返回 s 中涵盖 t 所有字符的最小子串。如果 s 中不存在涵盖 t 所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串 "" 。* 注意:如果 s 中存在这样的子串,我们保证它是唯一的答案。** 输入:s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC"* 输出:"BANC"** @param {string} s* @param {string} t*/function minWindow(s, t) {// 初始化两个指针let left = 0;let right = 0;// 首先将 t 中元素存入 map 中,记录每个元素所需要的个数const needsMap = new Map();for (let char of t) {needsMap.set(char, needsMap.has(char) ? needsMap.get(char) + 1 : 1);}// 记录一个当前所需匹配值数,默认为 t 的长度let currentNeedLen = t.length;// 存储返回结果let resStr = '';// 滑动右指针while (right <= s.length) {const c1 = s[right];// 消费 map 中的数据,将所需个数匹配至 0if (needsMap.has(c1)) {needsMap.set(c1, needsMap.get(c1) - 1);// 如果对应的元素还需个数为0,则表示已经的值包含了该元素所有个数if (needsMap.get(c1) === 0) currentNeedLen -= 1;}// 移动左指针以缩小字符串长度while (currentNeedLen === 0) {const newStr = s.slice(left, right + 1);resStr = !resStr || resStr.length > newStr.length ? newStr : resStr;const c2 = s[left];// 如果剔除的左边元素剔除后对于匹配元素无影响,则可以继续剔除if (needsMap.has(c2)) {needsMap.set(c2, needsMap.get(c2) + 1);if (needsMap.get(c2) === 1) {currentNeedLen += 1;}}left += 1;}// 向右移动右指针right++;}return resStr;}console.log(minWindow('ADOBECODEBANC', 'ABC'));
树
树通常用来表征结构化具有层级特征的数据,例如公司组织架构,中国省市区县层级划分等数据均可使用树这一数据结构呈现与存储。
以省市区县为例,可以用树这样来表示:
湖北省||--武汉市| || |--洪山区|||--黄冈市
在 JavaScript 语言中,表示树可以有几种形式
- 将树中同一层级树节点存储在数组中
- 通过指针连接各节点
形式一我们可以像如下进行表示:
const provinces = [{name: '湖北省',children: [{name: '武汉市',children: [{name: '洪山区',},],},{name: '黄冈市',},],},];
这种形式可以轻易表示多叉树。
形式二我们可以像如下进行表示:
const data = {value: 0,left: {value: 1,left: {value: 3,},},right: {value: 2,},};
通过这种形式,可以轻易表示二叉树。
基础算法
基础算法包括树的遍历,这里介绍树的层级遍历、深度优先遍历。
多叉树
层级遍历
层级遍历通常用来遍历多叉树,遍历过程可借助队列这一数据结构实现,代码如下:
function traverse(tree) {const stack = [];stack.push(tree);while (stack.length) {const current = stack.shift();console.log(current.value);if (current.children)current.children.forEach(te => {stack.push(te);});}}const treeData = {value: 0,children: [{value: 1,children: [{value: 3,},{value: 4,},],},{value: 2,},],};traverse(treeData);// 代码输出:0 1 2 3 4
深度遍历
深度遍历我们首先能想到通过递归实现,因为递归本身就是基于函数栈这一原理实现。同时我们还可以通过栈这一数据结构,完成树的深度遍历。
- 递归实现
function traverse(tree) {console.log(tree);if (tree.children) {tree.children.forEach(traverse1);}}const treeData = {value: 0,children: [{value: 1,children: [{value: 3,},{value: 4,},],},{value: 2,},],};traverse(treeData);
二叉树
二叉树的遍历也可分为层级遍历、前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历。此处前中后序表示访问根节点的时机,例如前序遍历表示先访问根节点,然后访问左子树,最后访问右子树。
递归实现前中后序遍历
// 前序遍历function preTraverse(tree) {if (!tree) return;console.log(tree.value);preTraverse(tree.left);preTraverse(tree.right);}// 中序遍历function inTraverse(tree) {if (!tree) return;inTraverse(tree.left);console.log(tree.value);inTraverse(tree.right);}// 后序遍历function postTraverse(tree) {if (!tree) return;postTraverse(tree.left);postTraverse(tree.right);console.log(tree.value);}
非递归实现前中后序遍历
// 前序遍历function preTraverseStack(root) {const res = [];const stack = [];if (root) stack.push(root);while (stack.length) {const n = stack.pop();res.push(n.value);const { left, right } = n;if (right) stack.push(right);if (left) stack.push(left);}return res;}// 中序遍历function inTraverseStack(tree) {// 首先不断压栈到最左边子树let p = tree;const arr = [];const res = [];while (p || arr.length !== 0) {if (p) {// 如果 p 存在,则一直进行压栈arr.push(p);p = p.left;} else {// 当当前节点没有左子树时,则出栈let node = arr.pop();// 访问节点res.push(node.value);p = node.right;}}return res;}// 后序遍历function postTraverseStack(tree) {const arr = [tree];const res = [];while (arr.length !== 0) {let node = arr.pop();res.push(node.value);if (node.left) arr.push(node.left);if (node.right) arr.push(node.right);}return res.reverse();}
经典题
求二叉树的最大深度
例如考察二叉树的最大深度,则是在树的深度遍历基础上进行改进。示例如下
function maxDepth(root) {let res = 0;const dfs = (r, l) => {if (!r) return;res = Math.max(res, l);dfs(r.left, l + 1);dfs(r.right, l + 1);};dfs(root, 1);return res;}const data = {value: 1,left: {value: 2,left: {value: 3,},},right: {value: 4,},};console.log(maxDepth(data));
通过这个考题联想到另外一个,找出二叉树的所有路径。
function getTreeGraph(root) {const paths = [];const dfs = (r, path, p) => {if (!r) {// 其中 !p.left && !p.right 表示当前节点为叶子节点if (!p.left && !p.right && !paths.includes(path)) {paths.push(path);}return;}const { left: rLeft, right: rRight } = r;dfs(rLeft, `${path}${rLeft?.value ? `-${rLeft?.value}` : ''}`, r);dfs(rRight, `${path}${rRight?.value ? `-${rRight?.value}` : ''}`, r);};dfs(root, root.value, null);return paths;}const data = {value: 1,left: {value: 2,left: {value: 3,},},right: {value: 4,},};console.log(getTreeGraph(data));// 输出:[ '1-2-3', '1-4' ]
将二叉树节点存储到数组中
有两种方法,代码实现如下:
function levelOrder(root) {if (!root) return [];const nodes = [[root, 0]];const result = [];while (nodes.length) {const [n, l] = nodes.shift();if (result[l]) {result[l].push(n.value);} else {result[l] = [n.value];}if (n.left) nodes.push([n.left, l + 1]);if (n.right) nodes.push([n.right, l + 1]);}return result;}
或者
function levelOrder(root) {if (!root) return [];const q = [root];const result = [];while (q.length) {let len = q.length;result.push([]);while (len--) {const n = q.shift();result[result.length - 1].push(n.value);if (n.left) q.push(n.left);if (n.right) q.push(n.right);}}return result;}
测试如下
const data = {value: 1,left: {value: 2,left: {value: 3,},},right: {value: 4,},};console.log(levelOrder(data));// 输出树层级/*** [* [1],* [2, 4],* [3]* ]*/
图
通常使用邻接矩阵、邻接表或关联矩阵表示图的节点与边信息。
邻接矩阵:
A B C DA 0 1 0 0B 1 0 1 0C 0 1 0 0D 0 0 0 0
邻接表:
{0: [1, 2],1: [2, 3],2: [3],3: [1]}
通常,我们倾向使用邻接表表征图。
基础算法
图的深度优先遍历
给定邻接表表示图:
const graph = {0: [1, 2],1: [2],2: [0, 3],3: [3],};
通过深度优先遍历方式,遍历该图。
function graphDepthVisit(g, n) {const visited = new Set();function dfs(n) {console.log(n);visited.add(n);g[n].forEach(e => {if (!visited.has(e)) {dfs(e);}});}dfs(n);}graphDepthVisit(graph, 1);// 1 2 0 3
图的广度优先遍历
function graphBreadthVisit(g, n) {const q = [n];const visited = new Set(q);while (q.length) {const c = q.shift();console.log(c);g[c].forEach(e => {if (!visited.has(e)) {q.push(e);visited.add(e);}});}}graphBreadthVisit(graph, 2);// 2 0 3 1
堆
堆本质是树,是完全二叉树。堆可以分为最小堆、最大堆。
- 最小堆:每个根节点值都小于其子节点值
- 最大堆:每个根节点值都大于其子节点值
在 JavaScript 中,可以使用数组来存储堆。
.1(0)3(1) 6(2)5(3) 9(4) 8(5)
存储如:[1, 3, 6, 5, 9, 8]
存储有以下特点:
- 左侧子节点在数组中存储位置是 2 * index + 1;
- 右侧子节点在数组中存储位置是 2 * index + 2;
- 父节点在数组中存储位置是 (index - 1) / 2;
主要应用
- 堆能高效、快速地找到最大(小)值,时间复杂度为 o(1)
- 找出第 K 个最大(小)元素
基础算法
构建最小堆,完成元素插入、删除。有两个核心算法需要注意:
- 插入时,插入值不断上移,直至满足堆条件
- 删除时,先将堆尾元素填补在堆首,然后不断下移,直至满足堆条件
构建一个最小堆,代码如下:
class MinHeap < E > {/*** Storage heap data*/private heap: E[];constructor() {this.heap = [];}/*** get current superior element index* @param index* @returns*/private getSuperiorIndex(index: number) {return (index - 1) >> 1;}/*** get current subordinate index* @param index* @returns*/private getSubordinateIndexs(index: number) {return [index * 2 + 1, index * 2 + 2];}/*** swap* @param i1* @param i2*/private swap(i1: number, i2: number) {const temp = this.heap[i1];this.heap[i1] = this.heap[i2];this.heap[i2] = temp;}/*** Move element up* @param index*/private moveUp(index: number) {if (index === 0) return;const superiorIndex = this.getSuperiorIndex(index);if (this.heap[superiorIndex] > this.heap[index]) {this.swap(superiorIndex, index);this.moveUp(superiorIndex);}}/*** Move element down* @param index*/private moveDown(index: number) {const subIndexs = this.getSubordinateIndexs(index);subIndexs.forEach(subIndex => {if (this.heap[subIndex] < this.heap[index]) {this.swap(subIndex, index);this.moveDown(subIndex);}});}/*** Insert data into heap* @param value*/insert(value: E) {this.heap.push(value);// Adjust data locationthis.moveUp(this.heap.length - 1);}/*** Pop up top element*/pop() {if (!this.size()) return;this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop() as E;this.moveDown(0);}/*** peek heap* @returns E*/peek() {return this.heap[0];}/*** return heap size* @returns number*/size() {return this.heap.length;}}const minHeap = new MinHeap < number > ();minHeap.insert(3);minHeap.insert(2);minHeap.insert(1);minHeap.pop()
经典题
返回给定数组第 K 大元素
// 使用最小堆const minHeap = new MinHeap();// 给定数据const data = [3, 2, 1, 5, 6, 4];// k = 2,第2大元素data.forEach(d => {minHeap.insert(d);if (minHeap.size() > 2) {minHeap.pop();}});minHeap.peek();
数组中前 K 个高频元素
给定 [1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 3]及 k=2,返回[1, 2]
此题通过 map 与最小堆辅助完成。
function topFrequent(nums, k) {const minHeap = new MinHeap();const map = new Map();nums.forEach(d => {map.set(d, map.get(d) ? map.get(d) + 1 : 1);});map.forEach((value, key) => {minHeap.insert({value,key,});if (minHeap.size() > k) {minHeap.pop();}});return minHeap.heap.map(h => h.key);}console.log(topFrequent([2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 4, 3], 2));
此处 MinHeap 在上移和下移操作中做了细微调整,如下:
this.heap[superiorIndex] &&this.heap[superiorIndex].value > this.heap[index].value;
以及
this.heap[subIndex] && this.heap[subIndex].value < this.heap[index].value;
合并 K 个排序链表